Metal 3d printing or additive manufacturing (AM) is a subset of the more general materials science and engineering class known as powder bed fusion or PBF. Both AM or metal 3d printing and PBF share the same basic premise. By overlaying subsequent layers of material precisely controlled manner, one can build any desired shape from a mound of powdered material.
How does it work?
Metal 3d printing is a process for creating three-dimensional objects from a digital design. Most metal 3D prints are done with laser sintering, a process in which a laser fuses powdered metal. Other methods, known as binder jetting and powder bed fusion, use binders and powdered materials, respectively, instead of a laser.
The printer works by melting the powdered metal on a platform. The melted metal is then pushed in layers, and the platform moves up for the next layer. The process is repeated until an object is formed. The resolution of 3D printers varies, but metal printers tend to use lasers with 1,500 watts of output power.
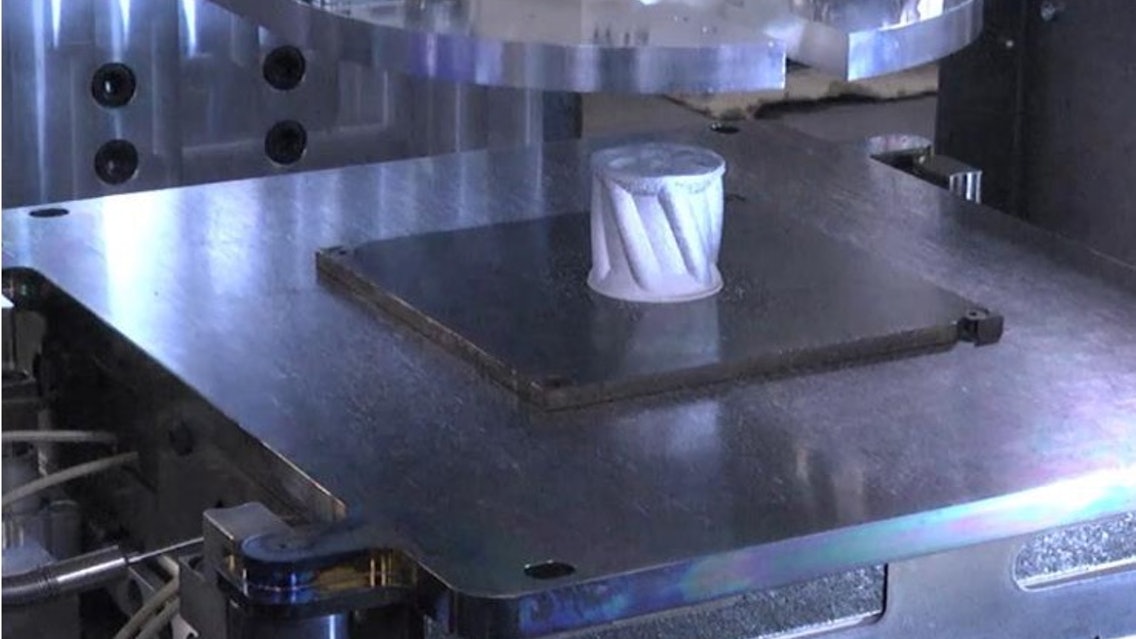
Metal 3D printers use a variety of techniques to create a three-dimensional object. The most common uses lasers to fuse powdered metal. Other methods, such as binder jetting and powder bed fusion, use binders and powdered materials, respectively, instead of a laser. The printer works by melting the powdered metal on a platform. The melted metal is then pushed in layers, and the platform moves up for the next layer. The process is repeated until an object is formed. The resolution of metal 3d printing varies, but metal printers tend to use lasers with 1,500 watts of output power.
Metal 3D printers use a variety of techniques to create a three-dimensional object. The most common uses lasers to fuse powdered metal. Other methods, such as binder jetting and powder bed fusion, use binders and powdered materials, respectively, instead of a laser. The printer works by melting the powdered metal on a platform. The melted metal is then pushed into layers, and the platform moves up.
Product development and innovation
Product development is risky. It takes a long time, so one has to gamble that their gamble will eventually pay off. But one has to gamble. Even when one does, it doesn’t often pay off. Product development is not like gambling. A roulette wheel has thirty different numbers on it, and the odds are roughly thirty to thirty-two. One will win. Thirty-two chances out of three. Product development is more like buying a lottery ticket. Every time one buys one, the odds are fifty-fifty.
But even the lottery is not entirely random. One knows the odds. One knows the odds of getting quintuple-jacks, for example, are about thirty thousand to one. But one still buys the ticket. Product development is like buying lottery tickets. One has to gamble and gamble a lot, but one also has to gamble smart.
But even if one gambled perfectly, one still wouldn’t always win. There are about two hundred kinds of lottery tickets. And the odds of getting one are roughly two hundred to one. When one gambles, one may still have to walk away. Or one may be right. But one won’t know until it’s too late.







